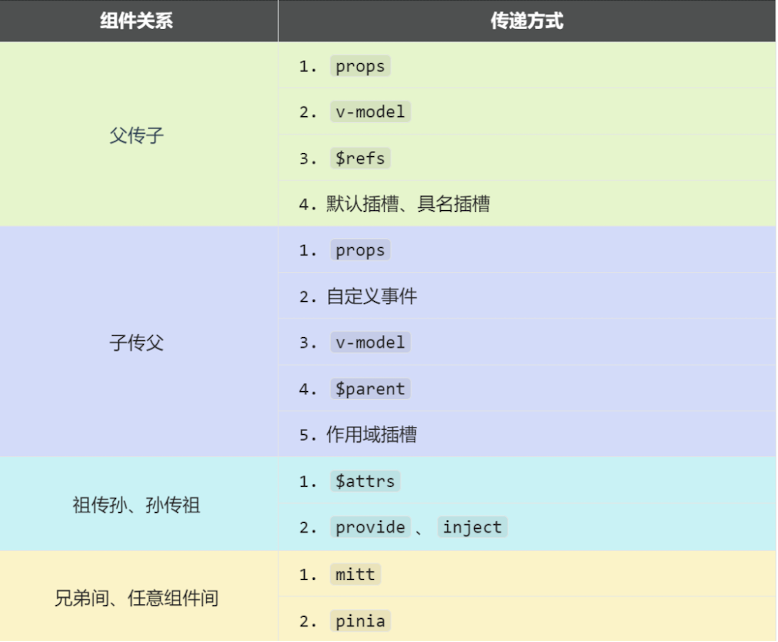
个人体验上常用的是:
props
v-model
slot
自定义事件
pinia
这几个得好好掌握
props
概述:props是使用频率最高的一种通信方式,常用与 :父 ↔ 子。
若 父传子:属性值是非函数。
若 子传父:属性值是函数。
父组件:
<template>
<div class="father">
<h3>父组件,</h3>
<h4>我的车:{{ car }}</h4>
<h4>儿子给的玩具:{{ toy }}</h4>
<Child :car="car" :sendToy="getToy"/>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="Father">
import Child from './Child.vue'
import { ref } from "vue";
// 数据
const car = ref('奔驰')
const toy = ref()
// 方法
function getToy(value:string){
toy.value = value
}
</script>子组件:
<template>
<div class="child">
<h3>子组件</h3>
<h4>我的玩具:{{ toy }}</h4>
<h4>父给我的车:{{ car }}</h4>
<button @click="sendToy(toy)">玩具给父亲</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="Child">
import { ref } from "vue";
const toy = ref('奥特曼')
defineProps(['car','sendToy'])
</script>自定义事件
概述:自定义事件常用于:子 => 父。
注意区分好:原生事件、自定义事件。
原生事件:
事件名是特定的(
click、mosueenter等等)事件对象
$event: 是包含事件相关信息的对象(pageX、pageY、target、keyCode)
自定义事件:
事件名是任意名称
事件对象
$event: 是调用emit时所提供的数据,可以是任意类型!!!
普通写法:
父组件:
<template>
<div class="father">
<Child :car="car" @send-toy="getToy"/>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from "vue";
// ... 其他代码
const toy = ref();
// 这个函数将接收子组件通过 emit 传递过来的参数
function getToy(value: string){
console.log('子组件传来的值:', value); // e.g., '奥特曼'
toy.value = value; // 修改父组件自身的状态
}
</script>子组件:
<template>
<div class="child">
<button @click="emit('sendToy', toy)">玩具给父亲</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue';
const toy = ref('奥特曼');
// 使用 defineEmits 声明组件可以触发的事件
const emit = defineEmits(['sendToy']); // 声明一个名为 'sendToy' 的事件
</script>最佳实践
父组件:
<template>
<div class="father">
<h3>父组件,</h3>
<h4>我的车:{{ car }}</h4>
<h4>儿子给的玩具:{{ toy }}</h4>
<Child :car="car" @send-toy="getToy"/>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="Father">
import Child from './Child.vue'
import { ref } from "vue";
const car = ref('奔驰')
const toy = ref()
// getToy 方法现在是事件的回调函数,它会自动接收子组件传递的数据
function getToy(value:string){
toy.value = value
}
</script>子组件:
<template>
<div class="child">
<h3>子组件</h3>
<h4>我的玩具:{{ toy }}</h4>
<h4>父给我的车:{{ car }}</h4>
<button @click="emit('send-toy', toy)">玩具给父亲</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="Child">
import { ref } from "vue";
const toy = ref('奥特曼')
// 1. 使用 defineEmits 声明并获取事件触发器
const emit = defineEmits<{
(e: 'send-toy', value: string): void // 推荐使用类型化 Emits
}>()
// 2. 推荐使用类型化 Props
defineProps<{
car: string
}>()
</script>mitt
概述:与消息订阅与发布(pubsub)功能类似,可以实现任意组件间通信。
安装mitt
npm i mitt
新建文件:src\utils\emitter.ts
// 引入mitt
import mitt from "mitt";
// 创建emitter
const emitter = mitt()
/*
// 绑定事件
emitter.on('abc',(value)=>{
console.log('abc事件被触发',value)
})
emitter.on('xyz',(value)=>{
console.log('xyz事件被触发',value)
})
setInterval(() => {
// 触发事件
emitter.emit('abc',666)
emitter.emit('xyz',777)
}, 1000);
setTimeout(() => {
// 清理事件
emitter.all.clear()
}, 3000);
*/
// 创建并暴露mitt
export default emitter
接收数据的组件中:绑定事件、同时在销毁前解绑事件:
import emitter from "@/utils/emitter";
import { onUnmounted } from "vue";
// 绑定事件
emitter.on('send-toy',(value)=>{
console.log('send-toy事件被触发',value)
})
onUnmounted(()=>{
// 解绑事件
emitter.off('send-toy')
})
【第三步】:提供数据的组件,在合适的时候触发事件
import emitter from "@/utils/emitter";
function sendToy(){
// 触发事件
emitter.emit('send-toy',toy.value)
}
注意这个重要的内置关系,总线依赖着这个内置关系
v-model
概述:实现 父↔子 之间相互通信。
前序知识 ——
v-model的本质
<!-- 使用v-model指令 -->
<input type="text" v-model="userName">
<!-- v-model的本质是下面这行代码 -->
<input
type="text"
:value="userName"
@input="userName =(<HTMLInputElement>$event.target).value"
>组件标签上的
v-model的本质::moldeValue+update:modelValue事件。
<!-- 组件标签上使用v-model指令 -->
<myInput v-model="userName"/>
<!-- 组件标签上v-model的本质 -->
<myInput :modelValue="userName" @update:model-value="userName = $event"/>myInput组件中:
<template>
<div class="box">
<!--将接收的value值赋给input元素的value属性,目的是:为了呈现数据 -->
<!--给input元素绑定原生input事件,触发input事件时,进而触发update:model-value事件-->
<input
type="text"
:value="modelValue"
@input="emit('update:model-value',$event.target.value)"
>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="myInput">
// 接收props
defineProps(['modelValue'])
// 声明事件
const emit = defineEmits(['update:model-value'])
</script>也可以更换
value,例如改成abc
<!-- 也可以更换value,例如改成abc-->
<myInput v-model:abc="userName"/>
<!-- 上面代码的本质如下 -->
<myInput :abc="userName" @update:abc="userName = $event"/>myInput组件中:
<template>
<div class="box">
<input
type="text"
:value="abc"
@input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="myInput">
// 接收props
defineProps(['abc'])
// 声明事件
const emit = defineEmits(['update:abc'])
</script>如果
value可以更换,那么就可以在组件标签上多次使用v-model
<myInput v-model:abc="userName" v-model:xyz="password"/>$attrs
概述:
$attrs用于实现当前组件的父组件,向当前组件的子组件通信(祖→孙)。具体说明:
$attrs是一个对象,包含所有父组件传入的标签属性。注意:
$attrs会自动排除props中声明的属性(可以认为声明过的props被子组件自己“消费”了)
父组件:
<template>
<div class="father">
<h3>父组件</h3>
<Child :a="a" :b="b" :c="c" :d="d" v-bind="{x:100,y:200}" :updateA="updateA"/>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="Father">
import Child from './Child.vue'
import { ref } from "vue";
let a = ref(1)
let b = ref(2)
let c = ref(3)
let d = ref(4)
function updateA(value){
a.value = value
}
</script>子组件:
<template>
<div class="child">
<h3>子组件</h3>
<GrandChild v-bind="$attrs"/>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="Child">
import GrandChild from './GrandChild.vue'
</script>孙组件:
<template>
<div class="grand-child">
<h3>孙组件</h3>
<h4>a:{{ a }}</h4>
<h4>b:{{ b }}</h4>
<h4>c:{{ c }}</h4>
<h4>d:{{ d }}</h4>
<h4>x:{{ x }}</h4>
<h4>y:{{ y }}</h4>
<button @click="updateA(666)">点我更新A</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="GrandChild">
defineProps(['a','b','c','d','x','y','updateA'])
</script>$refs,$parent
概述:
$refs用于 :父→子。$parent用于:子→父。
原理如下:
provide,inject
概述:实现祖孙组件直接通信
具体使用:
在祖先组件中通过
provide配置向后代组件提供数据在后代组件中通过
inject配置来声明接收数据
具体编码:
【第一步】父组件中,使用
provide提供数据
<template>
<div class="father">
<h3>父组件</h3>
<h4>资产:{{ money }}</h4>
<h4>汽车:{{ car }}</h4>
<button @click="money += 1">资产+1</button>
<button @click="car.price += 1">汽车价格+1</button>
<Child/>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="Father">
import Child from './Child.vue'
import { ref,reactive,provide } from "vue";
// 数据
let money = ref(100)
let car = reactive({
brand:'奔驰',
price:100
})
// 用于更新money的方法
function updateMoney(value:number){
money.value += value
}
// 提供数据
provide('moneyContext',{money,updateMoney})
provide('car',car)
</script>注意:子组件中不用编写任何东西,是不受到任何打扰的
【第二步】孙组件中使用inject配置项接受数据。
<template>
<div class="grand-child">
<h3>我是孙组件</h3>
<h4>资产:{{ money }}</h4>
<h4>汽车:{{ car }}</h4>
<button @click="updateMoney(6)">点我</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="GrandChild">
import { inject } from 'vue';
// 注入数据
// 注入 moneyContext,包含响应式 money (ref) 和 updateMoney 方法
// 提供了第二个参数作为默认值(当父组件未提供时使用),增强健壮性
const { money, updateMoney } = inject<MoneyContext>('moneyContext', {
money: ref(0), // 默认值使用 ref
updateMoney: (x: number) => {
console.log('未找到 updateMoney 方法,参数:', x)
}
})
// 注入 car,这是一个响应式对象 (reactive)
// 如果父组件没有提供,默认值将是一个非响应式对象
const car = inject('car', {
brand: '默认品牌',
price: 0
})! // 使用 ! 告诉 TypeScript 假定它一定会被提供(或处理默认值)
// ⚠️ 注意:注入的 money 是一个 Ref 对象,需要在 setup 中通过 .value 访问,但在模板中会自动解包。
// 注入的 car 是一个 Reactive 对象,可以直接像普通对象一样访问和修改属性。
</script>slot
默认插槽
父组件中:
<Category title="今日热门游戏">
<ul>
<li v-for="g in games" :key="g.id">{{ g.name }}</li>
</ul>
</Category>
子组件中:
<template>
<div class="item">
<h3>{{ title }}</h3>
<!-- 默认插槽 -->
<slot></slot>
</div>
</template>具名插槽
父组件中:
<Category title="今日热门游戏">
<template v-slot:s1>
<ul>
<li v-for="g in games" :key="g.id">{{ g.name }}</li>
</ul>
</template>
<template #s2>
<a href="">更多</a>
</template>
</Category>
子组件中:
<template>
<div class="item">
<h3>{{ title }}</h3>
<slot name="s1"></slot>
<slot name="s2"></slot>
</div>
</template>作用域插槽
理解:数据在组件的自身,但根据数据生成的结构需要组件的使用者来决定。(新闻数据在
News组件中,但使用数据所遍历出来的结构由App组件决定)具体编码:
父组件中:
<Game v-slot="params">
<!-- <Game v-slot:default="params"> -->
<!-- <Game #default="params"> -->
<ul>
<li v-for="g in params.games" :key="g.id">{{ g.name }}</li>
</ul>
</Game>
子组件中:
<template>
<div class="category">
<h2>今日游戏榜单</h2>
<slot :games="games" a="哈哈"></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts" name="Category">
import {reactive} from 'vue'
let games = reactive([
{id:'asgdytsa01',name:'英雄联盟'},
{id:'asgdytsa02',name:'王者荣耀'},
{id:'asgdytsa03',name:'红色警戒'},
{id:'asgdytsa04',name:'斗罗大陆'}
])
</script>